In this topic you will learn about concept of coordination, nervous coordination inhumans, sense organs, drugs and drug abuse in relation to nervous coordination, andcoordination in plants.
Concept of Coordination.
Coordination is the working together of the various organs of an organism in a systematic manner so as to produce a proper response to the stimuli. Without coordination the body becomes disorderly and it may fail to function properly.

The Ways in Which Coordination is Brought About
The coordination in simple multicellular animals takes place through nervous systemonly. The control and coordination in higher animals called vertebrates (including humanbeings) takes place through nervous system as well as hormonal system called endocrinesystem. Coordination in plants is under the control of hormones.
All the living organisms (plants and animals) respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli (singular: stimulus). The living organisms show response to stimuli such as light, heat, cold, sound, smell, taste, touch, pressure, pain,water, and force of gravity, etc. The ability to perceive, interpret and respond to stimuli is called irritability or sensitivity.
There are two types of stimuli:
- external
- internal.
External stimuli are associated with the surrounding environment such as wind temperature, light, pressure, touch, water and gravity.
Internal stimulioccur within the organism, for example, a decrease or an increase in the amount of water and glucose in the blood.
When an organism detects a stimulus, it initiates a response. A response is a behavioural,physiological or muscular activity initiated by a stimulus. For example, if a man touches a very hot utensil accidentally, he quickly pulls his hand away from the hot utensil. Here,heat is the stimulus and the man reacts (responds) by moving his hand away from the hot utensil. Similarly, when the sun is bright, we close our eyes. In this case, light is the stimulus and we react by closing our eyes. Likewise, when the amount of water in the blood drops, the pituitary gland secretes an anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) which stimulates the reabsorption of water in the kidneys.
Multicellular organisms detect stimuli through sense organs called receptors. A receptor is a sense organ (e.g. eye) or sensory nerve ending (e.g. in the skin or internal organ) which receives stimuli and sets nervous impulses. Impulses are electrical transmissions or chemical stimuli that are sent from the receptor to the coordinating system in the organism. The organs that respond to the stimuli are called effectors. A coordinator is an organ (e.g. the brain and spinal cord) that receives messages from the receptors,translates them and sends the information back to an effector for action. An effector is a muscle or gland which receives impulses from nerves, brain or spinal cord and responds to them. Response is the end-action, such as a muscle contracting to cause the movement of the arm. The diagram below illustrates the five components of coordination in mammals.
Nervous Coordination in Human , Neurons
Neurones
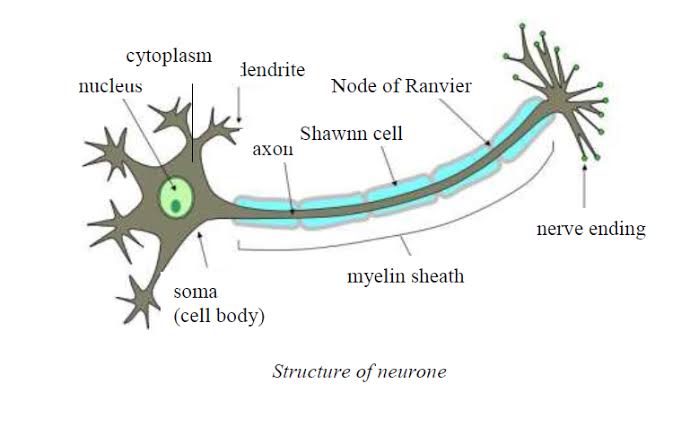
Neurones are nerve cells. They carry information as tiny electrical signals. A neuroneconsists of a cell body (with a nucleus and cytoplasm), dendrites that carry electricalimpulses to the cell, and a long axon that carries the impulses away from the cell. Theaxon of one neurone and the dendrites of the next neurone do not actually touch eachother.
The gap between neurones is called the synapse
Structure and functions of neurones
The diagram below shows a typical neurone: in this case, a motor neurone. It has tinybranches at each end (dendrites) and a long fibre (axon) that carries the signals or nervousimpulses. The axon is surrounded by a fatty layer known as the myelin sheath. Thishelps to protect the neurone and allow impulses to travel faster. The sheath is produces bySchawnn cells. The myelin sheath has nodes (Nodes of Ranvier) that speed uptransmission of nervous impulses. The cell body consists of cytoplasm enclosing thenucleus. There are also other organelles in the cytoplasm such as mitochondria thatsupply energy to for metabolic functions.
Synapses
Where two neurones meet, there is a tiny gap called a synapse. Signals cross this gapusing chemicals (neurotransmitters) released by a neurone. When the chemical diffusesacross the gap it makes the next neurone transmit an electrical signal. The transmission ofnervous impulses across synapses occurs thus:
- An electrical impulse travels along an axon.
- This triggers the nerve-ending of a neuron to release chemical messengers calledneurotransmitters.
- These chemicals diffuse across the synapse (the gap) and bind with receptormolecules on the membrane of the next neuron.
- The receptor molecules on the second neuron bind only to the specific chemicalsreleased from the first neuron. This stimulates the second neuron to transmit theelectrical impulse.

Types of neurones
There are three types of neurones namely motor neurone, sensory neurone and relay(or intermediate) neurone. Each of these neurones has a different structure and performsdifferent functions.
Motor neurone
A motor neurone is a nerve cell that transmits impulses from the central nervous system(CNS) to the effector organs such as muscles or glands where response is made. The cellbody of a motor neurone is at one end of the neurone and lies entirely within the centralnervous system (see the diagram above).
A sensory neurone is a nerve cell that transmits impulses from the receptors to the CNS.Sensory neurones have their cell bodies off the axon and outside the central nervoussystem.
Relay (intermediate or inter) neurone
A relay neurone conveys messages between neurones in the CNS. Relay neurones arelocated in the CNS between the sensory and the motor neurones.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The Meaning of Central Nervous System
Give the meaning of central nervous system
The CNS is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. Itcoordinates all the neural functions. The chart below shows subdivisions of the nervoussystem.

The brain
The human brain is a specialized organ that is ultimately responsible for all thought andmovement that the body produces. This allows humans to successfully interact with theirenvironment, by communicating with others and interacting with inanimate objects neartheir surroundings. If the brain is not functioning properly, the ability to move, generateaccurate sensory information or speak and understand language can be damaged as well.
The brain has many different parts. Each part has a unique function that allows humansobserve and interact with their environment effectively. The following are parts of thehuman brain and their functions:

Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain, and contains tools which are responsiblefor most of the brain’s function. It is divided into four sections: the temporal lobe, theoccipital lobe, parietal lobe and frontal lobe.
Parietal Lobe: Located in the cerebral hemisphere, this lobe focuses on comprehension.Visual functions, language, reading, internal stimuli, tactile sensation and sensorycomprehension are monitored here.
Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe controls visual and auditory memories. It includesareas that help manage some speech and hearing capabilities, behavioural elements, andlanguage. It is located in the cerebral hemisphere.
Occipital Lobe: the occipital lobe is located in the cerebral hemisphere in the back of thehead. It helps to control vision.

The Components of the Central Nervous System and their Functions
Identify the components of the central nervous system and their functions
The table below summarizes the structure and functions of the major components of the brain.
.




The Structure of the Spinal Cord and Brain
Spinal cord
The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between thebrain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independentlycontrol numerous reflexes and central pattern generators. It carries out two mainfunctions:
- It connects a large part of the peripheral nervous system to the brain. Information(nerve impulses) reaching the spinal cord through sensory neurons is transmitted upinto the brain. Signals arising in the motor areas of the brain travel back down thecord and leave in the motor neurones.
- The spinal cord also acts as a minor coordinating centre responsible for some simplereflexes like the withdrawal reflex.
The intermediate neurones carrying impulses to and from specific receptors and effectorsare grouped together in spinal tracts.
The diagram shows various sections of the spinal cord and the functions of each section.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The peripheral nervous system is made up of a network of nerves linking various parts ofthe body to the brain and spinal cord. It includes the cranial nerves, spinal nerves andtheir roots and branches, peripheral nerves, and neuromuscular junctions.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) has two components: the somatic nervous systemand the autonomic nervous system. The PNS consists of all of the nerves that lie outsidethe brain and spinal cord.
The Components of the Peripheral Nervous System and Their Functions
The somatic nervous system is made up of nerves that connect to voluntary skeletalmuscles and to sensory receptors. It is composed of afferent nerves that carryinformation to the central nervous system (spinal cord) and efferent nerves that carryneural impulses away from the central nervous system. This system is responsible for theinvoluntary control of the skeletal muscles, bones and sense organs.
The autonomic nervous system is further subdivided into sympathetic andparasympathetic nervous system.
- The sympathetic nervous system activates the ‗fight or flight’ response under suddenor stressful circumstances, for instances by raising the heart rate and dilating thepupils.
- The parasympathetic nervous system helps the body return to normal activity afteran emergency, which conserve energy and replenishes the system.
Together, these two systems regulate homeostasis within the body – one preparing thebody for action, and the other repairing the body afterward.
Reflex Action
When a receptor is stimulated, it sends a signal to the central nervous system, where thebrain co-ordinates the response. But sometimes a very quick response is needed, one thatdoes not need the involvement of the brain. This is a reflex action.
The reflex action is a rapid, involuntary response to a certain stimulus. The route that isfollowed by impulses during a reflex action is called a reflex arc.
Reflex actions are rapid and happen without us thinking. For example, you would pullyour hand away from a hot flame without thinking about it. The diagram below shows asimplified reflex arc.

This is what happens:
| 4 | It is acquired in one‘s life | It is inborn |
Modifying a reflex response
In some circumstances the brain can modify a reflex response. It does this by sending animpulse along a motor neuron of the reflex arc. This enables us, for example, to hold ahot dinner plate when normally we would drop it.
Sense Organs
Sense organs are organs of the body that detect and respond to changes in theenvironment (stimuli) so as to survive.
Types of Sense Organs and Their Relative Position
There are five sense organs in our body: eyes,ears, nose, tongue and skin. We receive a variety of information from the environment around us through the sense organs. The sense organs contain receptors. A receptor is a cell (or a group of cells) in a sense organ which is sensitive to a particular type of stimulus (or a particular type of change in the environment) such as light, sound, smell,taste, heat, pressure, etc. The different sense organs contain receptors for detecting different stimuli.
The eyes have light receptors (which can detect light), ears have sound receptors (which can detect sound), nose has smell receptors (which can detect smell), tongue has taste receptors (which can detect taste) whereas skin has receptors for detecting touch,pressure, heat (or cold) and pain, etc.
The Structure of Each Sense Organ
Describe the structure of each sense organ
The human eye
The eye is the organ for vision. The eye is one of the most complex parts of the body.The different parts of the eye allow the eye to take in light and perceive objects around using the proper color, detail and depth. This allows people to make more informed decisions about their environment. If a portion of the eye becomes damaged, you may not be able to see effectively. You may even lose your vision completely.Parts of the eye and their functions There are several physical and chemical elements that make up the eye. The table below shows different parts of the human eye and their functions.Eye part Description and function(s)Cornea The cornea is the outer, transparent covering of the eye. This layer protects the eye from elements that could cause damage to the inner parts of the eye. The cornea also helps to focus light on the retina at the back of the eye. Sclera The sclera is commonly referred to as the “white” of the eye. It protectsthe eye and maintains the shape of the eye ball.Pupil The pupil appears as a black dot in the middle of the eye. This black area is actually a hole that takes in light to enable the eye focus on the objects in front of it. The pupil, thus, controls the amount of light that enters the eye.Iris The iris contains the pigment which gives the eye its color. It has radial Internal structure

Parts of the eye and their functions
There are several physical and chemical elements that make up the eye. The table below shows different parts of the human eye and their functions.
Eye part
Description and function(s)
Cornea
The cornea is the outer, transparent covering of the eye. This layer protects the eye from elements that could cause damage to the inner parts of the eye. The cornea also helps to focus light on the retina at the back of the eye.
Sclera
The sclera is commonly referred to as the “white” of the eye. It protects the eye and maintains the shape of the eye ball.
Pupil
The pupil appears as a black dot in the middle of the eye. This black area is actually a hole that takes in light to enable the eye focus on the objects in front of it. The pupil, thus, controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Iris
The iris contains the pigment which gives the eye its colour. It has radial and circular muscles that control the size of the pupil by dilation and contraction. This allows the eye to take in more or less light depending on how bright it is around. The iris allows more light into the eye when the environment is dark and allows less light into the eye when the environment is bright.
Conjunctiva
This is a membrane that covers the cornea. It is thin and transparent so as to allow light to enter the eye. It is tough and protects the eye from mechanical damage.
Lacrimal glands
These glands are located on the outer corner of each eye. They produce tears which help moisten the eye when it becomes dry, and flush out particles which irritate the eye. As tears flush out potentially dangerous irritants, it becomes easier to focus properly.
Lens
This is a transparent structure filled with a jelly-like substance. The lens focuses light into the retina. It is held in place by the suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary muscles, which allow the lens to change shape depending on the amount of light entering the eye. Through the ciliary muscles, the lens becomes thicker to focus on nearby objects and thinner to focus on distant objects.
Retina
Retina is the sensory tissue that lines the inner layer of the eye. It is the layer of the eye where images are formed, and it is connected to the optic nerve that transmits the images to the brain to be interpreted. The retina is made up millions of photo receptors known as rods and cones.
Ciliary body
Ciliary body, also called ciliary muscles, is a ring-shaped tissue which holds and controls the movement of the eye lens, and thus, it helps to control the shape of the lens. The ciliary body contains glandular cells which secrete the aqueous humour.
Suspensory ligaments
The suspensory ligaments attach the lens to the ciliary muscles. When the ciliary muscles contract, they pull the suspensory ligaments and the lens gets long and thin to accommodate rays of light from distant objects. When the ciliary muscles relax, there is less tension on the suspensory ligaments and the lens becomes more spherical in shape. This enables the accommodation of light rays from near objects.
Choroid
The choroid lies between the retina and the sclera, which provides blood supply to the eye. Just like any other portion of the body, the blood supply gives nutrition to the various parts of the eye.
Vitreous humour
The vitreous humour is the gel located in the back of the eye which helps it hold its shape. This gel takes in nutrients from the ciliary body, aqueous humour and the retinal vessels so the eye can remain healthy. The gel in the vitreous humour is transparent to allow light to get to the retina and also helps maintain the shape of the eyeball.
Aqueous Humor
The aqueous humour is a watery substance that fills the eye. The aqueous humour gives the front of the eye its shape as well as nourishes the cornea and lens. This liquid is drained through the Schlemm canal so that any build-up in the eye can be removed. If the person’s aqueous humour is not draining properly, s/he can develop glaucoma.
Optic nerve
Optic nerve is a cranial nerve which contains sensory neurones. The neurones transmit impulses from the rods and cones of the retina to the brain for interpretation. The optic nerve exits the eye at the blind spot.
Blind spot
It is located at the point where the optic nerve leaves the eye. The blind spot is not sensitive to light because it has no rods or cones.
Fovea
The fovea is the centremost part of the macula*. This tiny area is responsible for our central, sharpest vision. A healthy fovea is important for reading, watching television, driving, and other activities that require the ability to see detail.*Small and highly sensitive part of the retina responsible for detailed central vision. The retina is the very centre of the macula.
Adaptations of the eye to its functions
The eye is adapted to its functions by possessing the following features:
- Conjunctiva, cornea and lens are transparent to allow light to pass through them.
- Sclerotic layer is made up of (collagen) fibres; it maintains shape of eyeball/protects the eye from mechanical damage.
- Cornea is transparent and curved thus refracts light rays and allows light to pass through.
- Choroid (a layer of a tissue) has black or dark pigments that prevent internal reflections of light in the eye.
- The eye contains blood vessels in the choroids layer that supply oxygen and nutrients to the eye, giving the eye energy to perform its function, and removes the metabolic wastes from the eye.
- Retina is made of photo receptors known as rods and cones, which trap light rays to enable the eye to do its function of vision.
- Yellow spot (fovea) has the highest concentration of cones for accurate and sharp,central vision.
- Optic nerve has sensory neurones for transmission of nerve impulses to the brain (forinterpretation).
- Lens is biconvex and made up of elastic, transparent material which adjusts to focus far or near objects and allows light rays to pass through.
- Suspensory ligaments are fibrous to hold the lens in place.
- . The ciliary body contains ciliary muscles which are contractile to for controlling the curvature and hence focal length of the lens. It also contains glands that secrete the aqueous and vitreous humours.
- The iris is opaque and contractile for controlling the amount of light entering the eye(by adjusting the size of the pupil).
- Ocular muscles coordinate eye movement so that both eyes can follow a moving object together.
- The eyelid covers an eye and prevents it from mechanical damage and invasion by foreign bodies.
- Eye lashes help to prevent dust and small insects or particles from entering the eyeby trapping them on their hairs.
- The presence of aqueous and vitreous humours helps the eye to bend light rays toward retina to process the signal and send impulse to the brain.
The Functions of Sense Organs and their Adaptive Features
Explain the functions of sense organs and their adaptive features
Adaptations of the eye to its functions
The eye is adapted to its functions by possessing the following features:
- Conjunctiva, cornea and lens are transparent to allow light to pass through them.
- Sclerotic layer is made up of (collagen) fibres; it maintains shape of eyeball/protects the eye from mechanical damage.
- Cornea is transparent and curved thus refracts light rays and allows light to pass through.
- Choroid (a layer of a tissue) has black or dark pigments that prevent internal reflections of light in the eye.
- The eye contains blood vessels in the choroids layer that supply oxygen and nutrients to the eye, giving the eye energy to perform its function, and removes the metabolic wastes from the eye.
- Retina is made of photo receptors known as rods and cones, which trap light rays tenable the eye to do its function of vision.
- Yellow spot (fovea) has the highest concentration of cones for accurate and sharp,central vision.
- Optic nerve has sensory neurones for transmission of nerve impulses to the brain (for interpretation).
- Lens is biconvex and made up of elastic, transparent material which adjusts to focus far or near objects and allows light rays to pass through.
- Suspensory ligaments are fibrous to hold the lens in place.
- . The ciliary body contains ciliary muscles which are contractile to for controlling the curvature and hence focal length of the lens. It also contains glands that secrete the aqueous and vitreous humours.
- The iris is opaque and contractile for controlling the amount of light entering the eye(by adjusting the size of the pupil).
- Ocular muscles coordinate eye movement so that both eyes can follow a moving object together.
- The eyelid covers an eye and prevents it from mechanical damage and invasion by foreign bodies.
- Eye lashes help to prevent dust and small insects or particles from entering the eye by trapping them on their hairs.
- The presence of aqueous and vitreous humours helps the eye to bend light rays toward retina to process the signal and send impulse to the brain.
The human ear
The ear is the organ of hearing and maintaining balance and posture. The outer ear protrudes away from the head and is shaped like a cup to direct sound waves toward the tympanic membrane, which transmits vibrations to the inner ear through a series of small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear called the malleus, incus and stapes. The inner ear, orcochlea, is a spiral-shaped chamber covered internally by nerve fibres that react to the vibrations and transmit impulses to the brain via the auditory nerve. The brain combines the input of our two ears to determine the direction and distance of sounds.
The inner ear has a vestibule system formed by three semicircular canals that are approximately at right angles to each other and which are responsible for the sense of balance and spatial orientation. The inner ear has chambers filled with a viscous fluid and small particles (otoliths) containing calcium carbonate. The movement of these particles over small hair cells in the inner ear sends signals to the brain that are interpreted asmotion and acceleration. The figure below shows the internal structure of the mammalian ear.
ear.

Adaptations of the mammalian ear to its functions
The ear is adapted to its functions by possessing the following features:
- The outer ear (pinna) is a flap of tissue which collects sound waves and directs them into the inner ear via the auditory canal.
- The lining of auditory canal contains wax-secreting cells which produce wax. The wax in the canal traps dust particles and other foreign bodies and hence protects thinner delicate parts of an ear from mechanical damage or microbial infections.
- The ear drum is thin and membranous, a fact that enables it to vibrate when sound waves hit it before converting the waves into vibrations and passing them on to the ear ossicles in the middle ear.
- The ear ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes) act as a lever system which can move forward and backward to amplify and transmit vibrations to the oval window.
- The Eustachian tube is hollow, a fact which allows air in and out of the middle ear to equalize the pressure between the inside and outside of the ear drum—which improves the drum‘s ability to vibrate
- The cochlea is coiled to increase the surface area for sound reception. It also caries auditory nerves which transmit sound impulses to the brain for interpretation drum skull bone semi-circular canals auditory canaleustachian tube round windowcochleaauditory nerve Internal structure of the human earoval window
- The presence of fluid-filled vestibular apparatus (semi-circular canals, sacculus, andutriculus) in the inner ear facilitates balancing of sound when the fluid is displaced.
The tongue
The tongue is an organ responsible for taste. It is the primary organ of taste (gustation), as much of its upper surface is covered in taste buds. The tongue’s upper surface is also covered with numerous lingual papillae. The tongue is sensitive and kept moist by saliva,and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels.
The receptors for taste, called taste buds, are situated chiefly in the tongue, but they are also located in the roof of the mouth near the pharynx. They are able to detect four basic tastes: salty, sweet, bitter, and sour.
Generally, the taste buds close to the tip of the tongue are sensitive to sweet and salty tastes, whereas those in the back of the tongue are sensitive to bitter tastes. The taste bud sin the sides of the tongue are sensitive to sour tastes. At the base of each taste bud there is a nerve that sends the sensations to the brain. The sense of taste functions in coordination with the sense of smell.
The number of taste buds varies substantially from individual to individual, but greater numbers increase sensitivity. Women, in general, have a greater number of taste buds than men. As in the case of color blindness, some people are insensitive to some tastes.

Adaptation of the tongue to its functions (as a sense organ)
The tongue is adapted to its functions by possessing the following features:
- The tongue has taste buds which help it to respond the stimuli such as sweet, bitter,sour and salty.
- At the base of each taste bud there is a nerve that sends the sensations to the brain.
The human nose
The nose is the organ responsible for the sense of smell. The cavity of the nose is lined with mucous membranes that have smell receptors connected to the olfactory nerve. The smells themselves consist of vapours of various substances. The smell receptors interact with the molecules of these vapours and transmit the sensations to the brain. The smell receptors are sensitive to seven types of sensations that can be characterized as camphor,musk, flower, mint, ether, acrid, or putrid. The sense of smell is sometimes temporarily lost when a person has a cold. Dogs have a sense of smell that is many times more sensitive than man’s.

When we want to ―smell‖ food we draw air high up into the nasal cavity where the chemicals come into contact with hairs on the sensory cells. Different chemicals stimulate different sensory cells and nervous impulses are set up which pass along theverves to the brain to be interpreted.
When our nose is blocked with cold, our food may become ―tasteless‖ because we no longer smell it.
Adaptations of the nose to its functions
The nose is adapted to its functions by possessing the following features:
- There are olfactory nerves, which carry impulse from the nose to the olfactory lobes of the brain for interpretation.The human nose
- Presence of mucus-secreting cells, which produce mucus that keep the surface of the nose moist.
- Presence of hairs in the nose helps the nose to trap dust particles and other foreign bodies. When the mucus is blown out from the nose, it carries the dust and other foreign bodies with it, thus preventing the olfactory organs from damage.
The human skin
The skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of theintegumentary system. The skin has multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards theunderlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. It protects us from microbesand the elements; helps regulate body temperature; and permits the sensations of touch,heat, and cold.
The skin has three layers:
- The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone
- The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands
- The deeper subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue.
The skin‘s colour is produced by special cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis.

The skin contains sensory nerve endings which are receptors. They are sensitive to pain,pressure, touch, heat and coldness. When the nerve endings are stimulated they set upnervous impulses which are sent to the spinal cord or brain to be interpreted.

Functions of skin
- Regulation: The skin plays an important role in regulation of body temperature inan organism thus helping to keep the body temperature constant (endothermic).
- The skin manufactures vitamin D through exposure to sunlight. Ergosterol in thefatty layer of the skin converts into vitamin D under the influence of sunlight.
- The skin produces melanin that protects the body from ultra violet radiationswhich can cause skin cancer.
- The skin acts as sensory organ due to the presence of various nerve endings.
- Protection: It prevents micro-organism and other foreign materials from enteringthe body.
- Excretion: Sweat glands produce sweat, which gets rid of excess heat, water, salts,some carbon dioxide and urea.
- Storage: Fat is a food store in the dermis.
Adaptations of the skin to its functions (as a sense organ)
The human skin is adapted to its sensory functions by having the following features:
- It has the hair erector muscle which controls whether the hair stands erect or liesdown depending on the temperature of the surrounding.
- It is supplied with nerves which convey impulses to the CNS to be interpreted.
- Presence of blood vessels (in the dermis) which dilate when the body temperature is high to facilitate heat loss by radiation and constrict when the temperature is low to reduce heat loss. The blood vessels also supply nutrients and oxygen to the skin and remove excretory products.
- The skin has sweat glands which produce sweat to help cool the body. During a hot day, the glands produce sweat (through sweat pores). Evaporation of the sweat uses the body heat and hence helps to cool down the body.
Drugs and Drug Abuse in Relation to Nervous Coordination
The Meaning of Drugs and Drug Abuse, in Relation to Nervous Coordination
Explain the meaning of drugs and drug abuse, in relation to nervous coordination
Drugs
A drug is any chemical substance, natural or synthetic, that has known physiological effects on humans or other animals. Foods are generally excluded from this definition, inspite of their physiological effects on animal species.
Most drugs, both useful and harmful, may affect the body (especially the brain), by altering the nerve cells’ natural reaction to these chemicals, or by mimicking the body’s normal compounds.
Some drugs slow down the passage of stimuli by affecting nerve cell membranes, and others act like neurotransmitters, perhaps passing stronger or longer-lasting impulses. As such they may alter the way sensory information is processed, or affect the thinking process.
Stimulants are drugs which speed up the action of the brain e.g. caffeine, found in tea and coffee. Sedatives are drugs which slow down the action of the brain e.g. alcohol. Eve none alcoholic drink will have some effect on the brain.
Proper Ways of Handling and Using Drugs
Outline proper ways of handling and using drugs
Proper use and handling of drugs
When using and handling drugs the following precautions must be observed:
- Avoid taking any drug without diagnosing the disease and prescription by the doctor.
- Always stay away from peer pressures and drug addicts to avoid copying their bad habits.
- Keep yourself busy with a number of activities such as sports and games, reading books, etc. Remember ‗an idle mind is the devil‘s workshop‘!
- Report any case of drug abuse or trafficking to concerned authorities.
- Form a counselling club to advise people especially youths on how to keep off from drugs.
- If one feels addicted, s/he should seek advice from health officials.
- Never take a dose more or less that what has been prescribed by the doctor.
- Complete the prescribed dose even after you start feeling well or after the symptoms of the disease has disappeared.9. Keep all drugs out of reach of children and drug addicts.
Drug addiction
Drug addiction refers to the compulsive and repeated use of increasing amounts of drugs with the appearance of withdrawal symptoms when drug use ceases. While drug use often begins as a way to seek recreation, the addictive properties of the drug make an addict crave for it permanently. This compulsion is uncontrollable and may interfere with aperson‘s everyday life. Even when the effects of drugs are damaging to a person‘s body and relationships with friends, family members and co-workers, the constant need for a drug often overcomes any rational thinking.
The human body has its own ability to produce some chemicals for its proper functioning. The continued use of the drug suppresses the body‘s ability to produce these chemicals or diminishes its production because these chemical are replaced by the drug.The body thus uses the drug as a substitute for its own natural chemicals. Since these chemicals are no longer produced, the body perceives that it needs the drug for its functioning. Therefore, a person craves for the drug so much that s/he feels cannot live without taking it. At this level the drug abuser becomes addicted to the drug. This miscalled drug addiction.
Causes and Effects of Drug Addiction
Like many mental health disorders, several causes may contribute to development of drug addiction and dependence. Some of the causes of drug abuse and addiction include the following:
- Some people take drugs to avoid physical or emotional pain, discomfort, stress,boredom, anxiety and depression.
- Some people also take drugs as a way to forget problems and life hardships they experience in life.
- Recreation: Drug users believe that taking drugs make them ‗feel better‘ and lively.
- Peer pressure leads people to drug so as to create a sense of belonging and fitting in the peer group. It‘s often said that teens use drugs when their friends do. Using drugs allows these young people to fit in with their peers and blend in with the crowd
- . Desire for a new experience and arousal: Some people just take drugs as an‗experiment‘ to find out the experience the drug users feel, but badly end unbecoming drug addicts.
- Lack of life and social skills, for example drug resistance skills that would help a person learn how to say no or avoid bad influence. People who are easy to copy habits from others, irrespective of the outcome of the given habit, can easily get into drug use.
Effects of drug abuse and addiction
Many illegal chemicals have extreme effects on the function of the brain, e.g. some drugs cause hallucinations – objects around you may change color, shape and size, or you may see and experience things that are not there at all. Such experiences may cause fear,depression, and mental disorders. Mostly, these substances alter one’s perception of reality.
Drugs produce a variety of short-term effects, but the most common ones include increased heart rate, high blood pressure, dizziness, tremors, mood changes and paranoia.In high dosages, the risk for more dangerous effects increases, and the potential for heart attack, stroke, respiratory failure and coma increases. The various effects of drug abuse include the following:
- Drugs confuse the mental faculties so that many drug users die in accidents, or overdose on the chemicals. Drugs can also induce them do dangerous activities such as unsafe sex or reckless driving.
- Many drugs induce a feeling of dependency (addiction) and are linked with criminal activity.
- Solvent abuse (sniffing glue, lighter fuel, etc.) – on which one can easily overdose -can cause death by heart failure.
- Other substances can incidentally affect the body’s “thermostat” – located in the hypothalamus (refer to a topic on homeostasis and osmoregulation) and cause death,following disruption of the body’s temperature control and regulation of the body’s water content. Even “legal” chemicals, such as alcohol (a “social” drug!), have adverse effects on the body.
- They can lead to aggressiveness, crime, violence and divorce.
- Sharing of needles used to inject drugs into the bloodstream cause HIV infections and hepatitis among the addicts. Likewise, because drugs impair one‘s judgement, it can lead to unprotected sex and hence become the cause of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases like syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and herpes.
- Drugs are very expensive to purchase. Therefore, the addicts spend much of their money on drugs at the expense of other family needs.
- Many drug addicts are weak and so they cannot participate in in-come generating activities. This leads to poverty, a fact which can lead to failure to meet one‘s basic needs.
- Drug addiction among women can lead to birth defects which include giving birth to small or premature babies or cause the baby to have withdrawal symptoms, birth defects or learning and behavioral problems. Additionally, illicit drugs may contain impurities that may be harmful to unborn baby
- Medical concerns like depression and anxiety can severely interrupt the addict‘ssocial and professional life, leading to mood swings, chronic fatigue and a diminished interest in former hobbies and important life events.
Preventive and Control Measures of Drug Abuse
Suggest preventive and control measures of drug abuse
Drug abuse is a serious psycho-sociological problem often difficult to be cured. The beltway to avoid these tragedies is to never start taking drugs. However, nowadays specific treatments are available for different types of mental illness. A regular, prolonged and sincere treatment is required .Social therapy or rehabilitation has got a very significant role. The following activities can be done for the control of drug addiction:
- Early detection, treatment and rehabilitation of drug addicts can help minimize the problem.
- Parents should set a warm and friendly atmosphere at home so that the drug users can feel easy to cooperate with.
- Motivation of the addicts to make up for detoxification.
- The youth should be motivated to get involved in the fight against drug abuse.
- Educating the community about the problems of drug addiction.
- Enforcement of laws, rules and regulation for the control and supply of drugs.
- The school curricula should contain courses about the drug addiction and drug abuse in detail (like the topic you are reading now).
- Various effects of drug addiction must be advertised through newspapers, radio,television, magazine, social media, and many other media so as to make the problem known to as many people as possible.
- The experience of drug users can be advertised to the people through media to make the general public aware of the effects of drugs so as to discourage those who might think of starting taking drugs.
Location of the Different Endocrine Glands in the Mammalian Body
Identify location of the different endocrine glands in the mammalian body
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
The endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones which regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction,sleep, and mood, among other functions. The glands are located in various parts of thehuman body. The function of these glands is to release various hormones, and as a whole,they are most commonly referred to as the endocrine system. These glands are pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thymus, pineal gland, testes, ovaries, thyroid, adrenal glands,parathyroid and pancreas. The location of these glands in the human body is as shown inthe diagrams below.
.

The role of Hormones produced by each Endocrine gland
Explain the role of hormones produced by each endocrine gland
The hormones released by glands of the endocrine system regulate the functions of many cells and organs as indicated in the following table.
Disorders of Hormonal Coordination in Mammals
Outline disorders of hormonal coordination in mammals
Causes of endocrine disorders
The causes of endocrine disorders are typically grouped into two categories:
- Endocrine disease that results when a gland produces too much or too little of an endocrine hormone, called a hormone imbalance.
- Endocrine disease due to the development of lesions (such as nodules or tumours) in the endocrine system, which may or may not affect hormone levels.
The endocrine’s feedback system helps control the balance of hormones in the bloodstream. If your body has too much or too little of a certain hormone, the feedback system signals the proper gland or glands to correct the problem. A hormone imbalance may occur if this feedback system has trouble keeping the right level of hormones in the bloodstream, or if your body doesn’t clear them out of the bloodstream properly.
Increased or decreased levels of endocrine hormone may be caused by:
- A problem with the endocrine feedback system.
- Disease.
- Failure of a gland to stimulate another gland to release hormones (for example, a problem with the hypothalamus can disrupt hormone production in the pituitary gland).
- A genetic disorder, such as multiple endocrine meoplasia or congenital hypothyroidism.
- Infection.
- Injury to an endocrine gland.
- Tumour of an endocrine gland.Most endocrine tumors and nodules (lumps) are non-cancerous. They usually do notspread to other parts of the body. However, a tumor or nodule on the gland may interfere with the gland’s hormone production.
Types of endocrine disorders
There are many different types of endocrine disorders. Majority of endocrine disorders cause the endocrine glands to produce too much (hypersecretion) or too low(hyposecretion) of a given hormone from a particular gland. Common problems that result from over secretion (hypersecretion) or under secretion (hyposecretion) of given hormones from given endocrine glands are explained below.
PITUITARY GLAND
Hypersecretion of growth hormone: Gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults.If the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, a child’s bones and body parts may grow abnormally fast.
Hyposecretion of growth hormone: Pituitary dwarfism – if the condition occurs during childhood, it slows down long bone growth.
Hypersecretion of ADH: Causes increased re absorption of water in the kidney tubules leading to production of a little urine but which is more concentrated.
Hyposecretion of ADH: Less water is absorbed from the glomeruli filtrate back to the body, leading to production of large volumes of dilute urine. This is called diuresis and isa symptom of diabetes inspidus.
THYROID GLAND
Hyperthyroidism
- Grave’s disease: The most common cause for an overactive thyroid is an autoimmune disorder called Grave’s disease. Grave’s disease, considered an autoimmune disease,shows elevated weight loss, nervousness, excessive perspiration, nervousness, highmetabolic rate and rapid, irregular heartbeat.
- Exophthalmos: protrusion of the eyeballs caused by oedematous tissue behind theeyes.
Hypothyroidism
- Cretinism (infantile hypothyroidism) – shows stunted growth, thickened facial features, abnormal bone development and mental retardation.
- Myxedema – low metabolic rate, lethargy (a condition characterized by extreme fatigue or drowsiness, or prolonged sleep patterns.), weight gain, increase in body fluids.
- Goitre – abnormal growth of the thyroid gland.
Hypersecretion of growth hormone: Gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults.If the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, a child’s bones and body parts may grow abnormally fast.
Hyposecretion of growth hormone: Pituitary dwarfism – if the condition occurs during childhood, it slows down long bone growth.
Hypersecretion of ADH: Causes increased re absorption of water in the kidney tubules leading to production of a little urine but which is more concentrated.
Hyposecretion of ADH: Less water is absorbed from the glomeruli filtrate back to the body, leading to production of large volumes of dilute urine. This is called diuresis and isa symptom of diabetes inspidus.
THYROID GLAND
Hyperthyroidism
- Grave’s disease: The most common cause for an overactive thyroid is an autoimmune disorder called Grave’s disease. Grave’s disease, considered an autoimmune disease,shows elevated weight loss, nervousness, excessive perspiration, nervousness, highmetabolic rate and rapid, irregular heartbeat.
- Exophthalmos: protrusion of the eyeballs caused by oedematous tissue behind theeyes.
Hypothyroidism
- Cretinism (infantile hypothyroidism) – shows stunted growth, thickened facial features, abnormal bone development and mental retardation.
- Myxedema – low metabolic rate, lethargy (a condition characterized by extreme fatigue or drowsiness, or prolonged sleep patterns.), weight gain, increase in body fluids.
- Goitre – abnormal growth of the thyroid gland.
PARATHYROID GLAND
Hyperparathyroidism: demineralization of bone resulting in possible bone deformity and fracture, and stones in the urinary tract
Hypoparathyroidism: decreased plasma calcium levels which can lead to severe muscletetany (a condition characterized by or resulting from uncontrolled muscle spasms).
PANCREAS
Hyperinsulinism: The liver is overstimulated to convert excess glucose to glycogen and fats for storage. This leads to low glucose concentration in the blood, a condition called hypoglycemia. This condition results in lack of glucose delivery to the brain causing disorientation, unconsciousness and even death (usually the result of an overdose ofinsulin).
Hypoinsulinism: Under-secretion of isulin causes very little glucose to be converted to glycogen and fats. This results in elevated glucose levels in the blood and urine. Thecondition is called hyperglycaemia, and is a symptom of diabetes mellitus. Over time,diabetics experience vascular and neural problems. Secondarily, poor circulation maylead to gangrene, blindness, kidney damage and impotence.
ADRENAL GLAND
Hypersecretion of corticosteroids: Cushing’s syndrome – changes in carbohydrate andprotein metabolism resulting in a puffy appearance.
Hyposecretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids: Addison‘s disease -symptoms of the disease include fatigue, stomach upset, hypoglycaemia, sodium andpotassium imbalance, dehydration, hypotension, and rapid weight loss. Death occurs withlack of treatment.
Hypersecretion of adrenaline: hypertension, obesity, headache, increased heartbeat,weak bones, hyperglycaemia, nervousness, sweating and early onset of sexual development.
Hyposecretion of adrenaline: low blood pressure, fatigue, muscular weakness, musclewasting, inability to withstand stress, and increased dark pigmentation of the skin.
OVARIES
Hypersecretion of oestrogen: Causes decreased sexual desire, heavy menstrual flow and increased weight in females.
Hyposecretion of oestrogen: Causes failure of females to develop some secondarysexual characteristics, poor development of the reproductive organs, liver, kidney andlungs.
TESTES
Hypersecretion of testosterone: Causes males to have female features such as enlargedbreasts and a wide pelvis.
Hyposecretion of testosterone: Causes failure of males to develop some secondarysexual characteristics, poor development of the reproductive organs and weak bones andmuscles.
THYMUS
Not responsible for any effects of hypo or hyper secretion of thymosin.
PINEAL
Not responsible for any effects of hypo or hyper secretion of melatonin.
Coordination in Plant, Concept of Tropic and Nastic Responses
The Concept of Tropic and Nastic Responses
Explain the concept of tropic and nastic responses
COORDINATION IN PLANTS
Both, plants and animals react (or respond) to various stimuli around them. But themethod of reacting to stimuli is not similar in plants and animals. They react to stimuli indifferent ways. For example, plants bend towards light but animals do not bend towardslight. The animal amoeba reacts to the presence of food by moving towards the foodparticle.
The plants do not have a nervous system and sense organs like eyes, ears, or nose, etc.,like the animals, but they can still sense things. The plants can sense the presence ofstimuli like light, gravity, chemicals, water, and touch, etc., and respond to them. Theysense these stimuli by using hormones in them.
The stimuli like light, gravity, chemicals, water, and touch, etc., are called environmental changes. So, we can also say that the plants coordinate their behaviour against environmental changes by using hormones. The hormones in plants do not act the sameway as in animals.
The hormones in plants coordinate their behaviour by affecting the growth of a plant.And the effect on growth of the plant can result in the movement of a part of the plantlike shoot (stem) or root, etc towards a certain stimulus.
Experiments to Investigate the Effects of Tropic and Nastic Responses in Plants
Carry out experiments to investigate the effects of tropic and nastic responses in plants
Plants receive and respond to a variety of stimuli that are important to their survival in the environment. These responses allow the plants to survive, grow, develop and reproduce.The movement of plants in the direction of stimulus is known as ‘tropism’. Tropisms aregrowth responses of plants that result in curvatures of plant organs toward or away fromcertain stimuli. Tropisms can be positive, in which case the plant will bend toward astimulus, or negative, in which case the plant will bend away from a stimulus.
The other movements shown by the plants are associated with the growth of the plants.For example, the shoot system moves towards sunlight and the root system towards earth.Thus, the plants also respond to their environment.
Important tropisms in plants include phototropism, geotropism, hydro tropism,chemo tropism and thigmotropism.
Phototropism
Phototropism is the tendency for plant organs to bend in response to a directional light source. For example, light streaming in a window from one direction will often cause the stems of plants placed nearby to bend toward the window, a positive phototropism.
Most plant shoots are positively phototropic because they tend to grow towards light.Most roots are negatively phototropic because they away from light.

The Importance of Tropic and Nastic Responses
Importance of phototropism
Phototropism is important to plants because of it enables the plant leaves to be placed under direct sunlight to absorb maximum light so as to carry out photosynthesiseffectively.
Geotropism
Geotropism is the movement of a part of the plant towards gravity. In most plants, roots-grow downward with gravity while shoots grow upward against gravity. Within hours,the shoot of a plant placed on its side will usually bend upward and the roots will benddownward as the plant reorients its direction of growth in response to gravity.
Most plant roots grow towards gravity and are said to be positively geotropic. Mostshoots grow away from gravity and are said be negatively geotropic.

Importance of geotropism
Geotropisms are important to plants because of the following reasons:
- It enables the plants to send roots into the ground hence anchoring the plant firmlyinto the soil.
- It enables plant roots to absorb water and mineral salts from the soil.
- Negative geotropism exhibited by the shoot enables the shoot to grow upwards, and in so doing, exposes the plant leaves to maximum sunlight for effective photosynthesis
Hydrotropism
Hydrotropism is the movement of a plant or part of a plant towards water. Plant roots normally grow towards moisture. They are therefore positively hydrotropic. If you plant a plant near a water source such as porous pot or river, the roots will always grow towardswater.

Importance of hydrotropism
It enables the plants to absorb dissolved minerals and water. Water is necessary forvarious functions such as:
- Photosynthesis
- Numerous physiological reactions that take place within plant cells.
- Turgor pressure, which aids in plant support.
- Dissolution of mineral salts.
Chemotropism

An example of positive and negative chemo-tropism is shown by a plant‘s roots; the roots grow towards useful minerals displaying positive chemo-tropism, and grow away fromharmful acids displaying negative chemo-tropism.
Chemotropism is the movement or growth of an organism or part of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. During the process of fertilization the movement of pollen tube towards ovule due to secretion of a sugary chemical in the ovary is an example of chemotropism
Importance of chemotropism
- It enables the plant to absorb mineral salts from the soil when the roots grow towards beneficial chemicals such as fertilizers.
- Negative geotropism, such as when plant roots grow away from the toxins, enables the plant to survive by avoiding contact with such harmful chemicals.
- . It facilitates the fertilization process in flowering plants.
Thigmotropism or haptotropism
Thigmotropsim refers to non-directional movements which take place neither towards noraway from the stimulus. The best example of nastic movement is folding and drooping ofleaves of Mimosa pudica plant when its leaves are touched with fingers or any object.The leaves fold even when swayed about by wind. Also the specialized touch-sensitivetendrils of many vining plants, such as pea, will bend toward the side receiving a touchstimulus. Continual stimulation can lead to the coiling of the tendril around an object,which enables vining plants to grasp objects on which they can climb


Importance of thigmotropism
- Thigmotropism enables crawling plants to climb up higher plants and expose their leaves to sunlight for optimum photosynthesis.
- It enables the insectivorous plants such as the Venus flytrap to trap insects and digestthem to obtain nutrients.